About
History
In 2004, research within the COMS group was focused on developing efficient, adaptive and accurate algorithms for polynomial and rational modeling of linear time-invariant (LTI) systems. This work resulted in a set of Matlab scripts that were used as a testing ground for new ideas and techniques. Research progressed, and with time these scripts were re-worked and refactored into one coherent Matlab toolbox, tentatively named the Multivariate MetaModeling (M3) Toolbox. The first public release of the toolbox (v2.0) occurred in November 2006.
For a list of changes since then refer to the changelog.
What is it used for
Global Surrogate Models
The SUMO-Toolbox was designed to solve the following problem:
In addition the toolbox provides powerful, adaptive algorithms and a whole suite of model types for
- data fitting problems (regression)
- response surface modeling
- interpolation
- model selection
- Design Of Experiments (DOE)
- model parameter optimization (hyperparameter selection)
- adaptive sample selection (also known as sequential design or active learning)
For an application scientist or engineer the toolbox provides a flexible, pluggable platform to which response surface modeling can be delegated. For researchers in surrogate modeling it provides a common framework to implement, test and benchmark new modeling and sampling algorithms.
See the Wikipedia Surrogate model page to find out more about these types of models.
Surrogate Driven Optimization
While the main focus of the toolbox is creating accurate global surrogate models, it can be used for other goals too.
For instance, the toolbox can be used to create and use a local surrogate model for optimization purposes. The information obtained from the surrogate model is used to guide the adaptive modeling process to the global optimum.
A sample strategy for optimization is a balance between local search, finding the optimum, and global search, refining the surrogate model. Such a sample strategy is implemented, see the different sampleselectors for more information.
What problems have been tackled?
The toolbox has already been applied successfully to a wide range of problems from domains as diverse as aerodynamics, geology, Electro-Magnetics (EM), engineering and economics.
Throughout the different problems, the input dimension has ranged from 1 to 96 and the output dimension from 1 to 10 (including both complex and real valued outputs). The number of datapoints has ranged from as little as 15 to as many as 50000.
Design Goals
During research into multivariate surrogate modeling techniques and algorithms it became clear that there was room for an adaptive tool that integrated different surrogate modeling approaches and did not tie the user down to one particular set of problems or techniques. More concretely, we were unable to find evidence of any projects that integrated:
- Building standalone global surrogate models (=replacement metamodels)
- Support for different model types, different model parameter optimization algorithms, different model selection criteria, ... (adaptive modeling)
- Sequential design (selecting data points iteratively and pro-actively)
- Distributed computing (integration with cluster and grid middleware to transparently run simulations in parallel)
- Usable implementation in software
This gave rise to a number of design goals that served as the guidelines for the design of the SUMO toolbox. These goals are:
- Development of a fully automated, adaptive surrogate model construction algorithm. Given a simulation model, the software should produce a replacement metamodel with as little user interaction as possible ("one button approach").
- There is no such thing as a "one-size-fits-all", different problems need to be modeled differently and require different levels of process knowledge. Therefore the software should be modular and extensible but not be too cumbersome to use or configure (sensible defaults).
- The toolbox should minimize the required prior knowledge of the system to be modeled.
- The algorithm should minimize the number of required samples in order to come to an acceptable surrogate model.
- The algorithm should terminate only when the predefined accuracy (set by the user) has been reached or the maximum number of iterations/samples has been exceeded.
Features
The main features of the toolbox are listed below. For an overview of recent changes see the Whats new page. A detailed list of changes can be found in the changelog.
| Implementation Language | Matlab, Java, and where appliccable C, C++ |
|---|---|
| Design patterns | Fully object oriented, with the focus on clean design and encapsulation. |
| Minimum Requirements | See the system requirements page |
| Supported data sources* | Local executable/script, simulation engine, Java class, Matlab script, dataset (txt file) (see Data format) |
| Supported data types | Supports multi-dimensional inputs and outputs. Outputs can be any combination of real/complex. |
| Configuration | Extensively configurable through one main XML configuration file. |
| Flexibility | Virtually every component of the modeling process can be configured, replaced or extended by a user specific, custom implementation |
| Predefined accuracy | The toolbox will run until the user required accuracy has been reached (on the selected measures), the maximum number of samples has been exceeded or a timeout has occurred |
| Model Types* | Out of the box support for:
|
| Model parameter optimization algorithms* | Pattern Search, Simulated Annealing, Genetic Algorithm, BGFS, DIRECT, Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), ... |
| Sample selection algorithms (=sequential design, active learning)* | Random, error based, density based, gradient based |
| Experimental design* | Latin Hypercube Sampling, Central Composite, Box-Behnken, random, dataset based, full factorial, adaptive (by doing a preliminary 1D screening in each dimension) |
| Model selection measures* | Validation set, cross-validation, leave-one-out, comparison on a grid, AIC |
| Sample Evaluation* | On the local machine (taking advantage of multi-core CPUs) or in parallel on a cluster/grid |
| Supported distributed middlewares* | Sun Grid Engine, LCG Grid middleware (both accessed through a SSH accessible frontnode) |
| Logging | Extensive logging to enable close monitoring of the modeling process. Logging granularity is fully configurable and log streams can be easily redirected (to file, console, a remote machine, ...). |
| Profiling* | Extensive profiling framework for easy gathering (and plotting) of modeling metrics (average sample evaluation time, hyperparameter optimization trace, ...) |
| Easy tracking of modeling progress | Automatic storing of best models and their plots. Ability to automatically generate a movie of the sequence of plots. |
| Available test problems* | Out of the box support for various built-in functions (Ackley, Camel Back, Goldstein-Price, ...) and datasets (Abalone, Boston Housing, FishLength, ...) from various application domains. Including a number of datasets (and some simulation code) from electronics. In total over 50 examples are available. |
* Custom implementations can easily be added
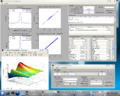
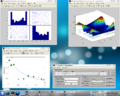
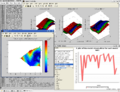
Screenshots
A number of screenshots to give you a feel of the toolbox. Note these screenshots do not necessarily reflect the latest toolbox version.
Movies
A number of movies that illustrate how modeling progresses as more samples come in. Note these movies do not necessarily reflect the latest toolbox version.
- Modeling the Step-Discontinuity problem
- Modeling the Ackley function
- ... more to come...
Documentation
- Poster: overview poster
- Presentation: slides
Mailing list
To stay up to date with the latest news and releases, we also recommend subscribing to our mailinglist here. Traffic will be kept to a minimum and you can unsubscribe at any time. (Note: due to technical reasons you will not be able to post on the mailing list)
Developers
The main contributors to SUMO-Toolbox are:
- Dirk Gorissen
- Karel Crombecq
- Ivo Couckuyt
Working under supervision of:
Previous contributors are:
References
See Citing the toolbox.